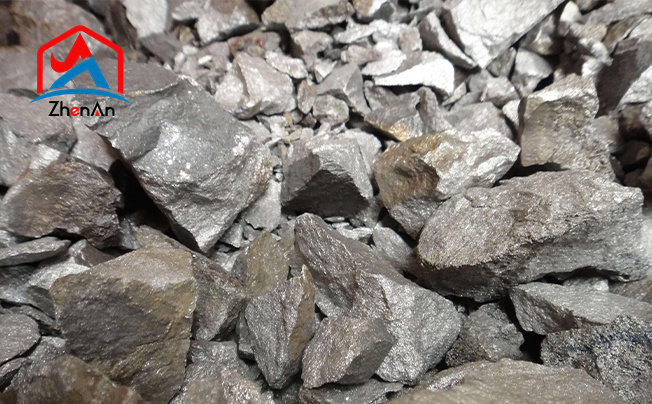
Ferromolybdenum is a ferroalloy consisting of iron and molybdenum. The top countries for ferromolybdenum manufacturing are China, the United States, and Chile, which together account for nearly 80% of the world's molybdenum ore production. It is produced by smelting a mixture of molybdenum concentrate and iron concentrate in a furnace. Ferromolybdenum is a versatile alloy that can be used in a variety of applications across different industries.
The largest application area for ferromolybdenum alloys is the production of ferrous metal alloys. Depending on the range of molybdenum content,
ferromolybdenum alloys can be used to make machine tools and equipment, military hardware, refinery piping, load-bearing components, and rotary drilling rigs.
Ferromolybdenum alloys are also used in cars, trucks, locomotives, and ships. Ferromolybdenum alloys are used in stainless and heat-resistant steels in synthetic fuels and chemical plants, heat exchangers, generators, refinery equipment, pumps, turbine piping, marine propellers, plastics, and acid storage containers.
Tool steels with higher molybdenum content are used for high-speed machining parts, drills, screwdrivers, dies, cold-working tools, chisels, heavy castings, rolls, cylinder blocks, ball mills and rolls, piston rings, and large drills.
There are two methods for producing ferromolybdenum. One is to produce high-carbon ferromolybdenum-based electric furnace carbon reduction blocks, and the other is to produce low-carbon ferromolybdenum-based ... (3) Finishing and furnace steam account for the largest proportion of returned iron, which needs to be smelted and recycled.
In-furnace metal thermal reduction method (generally known as silicon thermal reduction method): This is the simplest, most economical and most widely used method for producing ferromolybdenum.
This method uses silicon instead of carbon as a reducing agent for molybdenum oxide. Silicon is added in the form of ferrosilicon. The heat released by the reduction reaction can melt the generated alloy and slag. Therefore, no heat source needs to be added from the outside during the production process, and it is easy to achieve spontaneous reaction.
The primary task of ferromolybdenum production is to achieve a high molybdenum recovery rate.
(1) Recycling of
ferromolybdenum particles in slag. Usually, slag with high colloidal molybdenum is returned for smelting, and slag containing a large number of metal particles is crushed and then magnetically enriched and recovered.
(2) Recycling smoke. Wherever there is molybdenum fines, there should be strict and efficient dust removal equipment. When using bags for dust removal, the ash contains about 15% molybdenum that can be captured.
(3) Finishing and steam in the furnace are the largest proportion of returned iron, which needs to be returned to smelting and recycled.
Role of molybdenum in manufacturing:
The main use of molybdenum is to refine alloy steel, because molybdenum can reduce the eutectic decomposition temperature of steel, expand the quenching temperature range of steel, and never affect the hardening depth of steel.
Molybdenum is often used with other elements such as chromium, nickel, vanadium, etc. to make steel have uniform crystal structure, improve the strength, elasticity, wear resistance and impact strength of steel.
Molybdenum is widely used in smelting structural steel, spring steel, bearing steel, tool steel, stainless acid-resistant steel, heat-resistant steel and magnetic steel. In addition, molybdenum is applied to alloy cast iron to reduce the particle size of gray cast iron, improve the performance of gray cast iron at high temperature, and improve its wear resistance.
Role of molybdenum in agriculture:
Molybdenum is widely used in agriculture to increase crop yields, mainly because molybdenum is a key trace element that plays an important role in plant growth, development and metabolism. Here are some of the ways molybdenum is used in agriculture and how it can help increase crop yields:
Application of molybdenum fertilizer: Molybdenum fertilizer is a fertilizer containing molybdenum that can be applied to the soil or foliar spray to provide the molybdenum required by plants. The application of molybdenum fertilizer can improve the efficiency of nitrogen utilization by crops, promote nitrogen absorption and metabolism, and thus increase crop yields.
Improving soil pH: Molybdenum easily combines into insoluble compounds in acidic soils, which reduces the absorption and utilization rate of molybdenum by plants. Therefore, by improving soil pH to a suitable range, the effectiveness of molybdenum in the soil can be increased, which is beneficial to the absorption of molybdenum by crops.
Molybdenum requirements for different crops: Different crops have different requirements for molybdenum, so when applying fertilizer, it is necessary to apply it reasonably according to the requirements of different crops to ensure that crops can obtain enough molybdenum.
The role of molybdenum in nitrogen-fixing bacteria: Molybdenum is also important for the growth and metabolism of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which can convert nitrogen in the air into a form that can be used by plants. Therefore, by providing enough molybdenum, the activity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria can be promoted, the amount of nitrogen fixed in the soil can be increased, and the yield of crops can be increased.
In short, molybdenum and ferromolybdenum are indispensable elements and raw materials in modern social life.