Ferro Tungsten alloys usually refer to alloys composed of tungsten (W) and iron (Fe). Generally speaking,
tungsten-iron alloys are non-magnetic. This is because tungsten itself is a non-magnetic metal, and the iron content in tungsten-iron alloys is usually low, which cannot give the alloy significant magnetism.
Tungsten And Its Magnetism
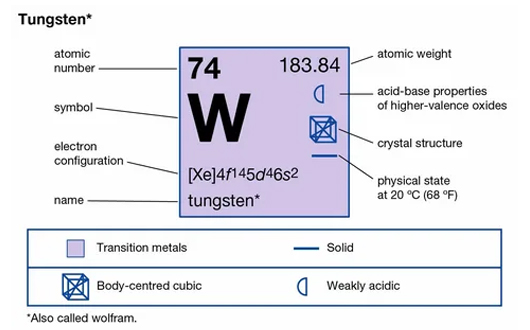
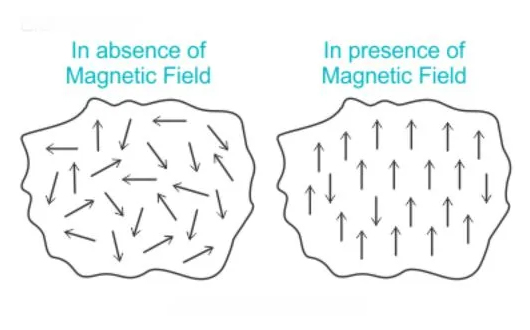
Tungsten, commonly referred to as tungsten, is a chemical element with atomic number 74 and symbol W. Magnetic elements are often called ferromagnetic elements, which are characterized by unpaired electrons. Tungsten also has electrons that are unpaired in its outer shell, allowing it to display some form of magnetism. The electrons move toward the external magnetic field, generating an electric moment that makes it slightly attractive to the magnetic field.
However, tungsten also has a dipole that moves in the opposite direction of the external influence, which prevents its magnetism. This makes it display paramagnetism.
Is Tungsten Alloy Magnetic?
Whether tungsten alloys can display magnetism depends on the metal they are fused to. These alloys are fused with a main metal along with various trace elements.
In fact, tungsten can be used to create many alloys which may have different magnetic properties.
For example, tungsten steel is magnetic because it contains steel containing ferromagnetic iron. This also contains trace amounts of vanadium and molybdenum along with at least 8% tungsten.
Tungsten carbide can also display magnetism, depending on the other metals used in the alloying process. Tungsten carbide requires a bonding metal to fuse properly and the choice of metal affects its magnetic properties. If cobalt or iron is incorporated into the alloy then it will be magnetic, on the other hand if nickel is used then it will be magnetic.
Factors Affecting Tungsten Magnetism
There are several factors that affect the magnetic properties of tungsten. These factors include:
Temperature: This factor relies on Curie's law which states that the magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is inversely proportional to the temperature. An increase in temperature reduces the magnetic susceptibility, which results in a decrease in the magnetic response. Low temperatures have the opposite effect and increase the magnetic properties of tungsten.
Applied magnetic field: An applied magnetic field affects the orientation of the electrons in tungsten. A strong magnetic field allows the element to acquire temporary weak magnetic abilities which disappear once the magnetic field is removed.
Binder content: For tungsten alloys, binder elements are used to melt the different elements. For example, cobalt is known to improve these properties, while nickel inhibits the already limited effect, making the element non-magnetic.
Composition: The exact composition of this element directly affects the magnetic properties of tungsten along with the number of unpaired electrons and the presence of dipoles and their arrangement.
Applications and Importance of Tungsten
As an important metallic element,
tungsten has a wide range of applications and importance in the fields of industry and science and technology. The following are the main applications and importance of tungsten:
1. High-temperature alloy manufacturing
Tungsten has high melting point and high strength properties, making it an important component in the manufacture of high-temperature alloys. These high-temperature alloys are commonly used in aerospace, aeroengines, nuclear energy and chemical industries, and can withstand extreme high temperature and pressure environments.
2. Cutting tools and abrasives
Due to the high hardness and wear resistance of tungsten, tungsten alloys are often used in the manufacture of cutting tools, drills, abrasives and grinding tools. These tools play an important role in metal processing, mining and other industrial fields.

3. Electronics industry
Tungsten is widely used in the electronics industry to manufacture electrodes, vacuum tubes, electronic devices and semiconductor devices. Its high melting point and stability make it one of the ideal materials for electronic devices.
4. Medical field
Tungsten alloys are used to manufacture medical devices, radiation protection materials and radiotherapy equipment. Its high density and radiation protection properties make it an important application in the medical field.
.jpg)
5. Nuclear energy field
Tungsten is widely used in the nuclear energy field to manufacture reaction control materials for nuclear reactors and other nuclear energy equipment. Its high density and melting point make it an ideal choice for nuclear energy materials.
6. Other applications
Tungsten is also used to manufacture high-density alloys, aerospace devices, optical lenses, automotive parts, etc. Its application in various industrial fields has made great contributions.
In short, tungsten, as an important engineering material, has unique physical and chemical properties, which makes it play a key role in many fields. Its high hardness, high melting point, corrosion resistance and dimensional stability make it one of the indispensable materials in various industrial and scientific fields. With the continuous development of science and technology, the application field of tungsten will continue to expand and make greater contributions to the progress and development of human society.

.jpg)